Ask Mark
Hot Tubs
How does a Heat Pump Work?
on
October 23, 2024

Operation Modes:
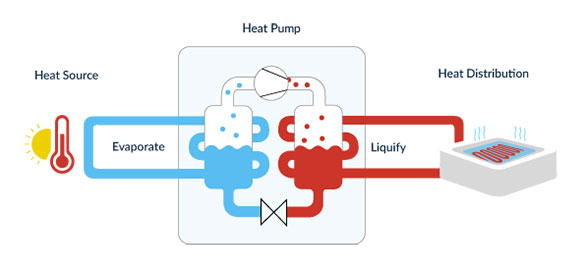
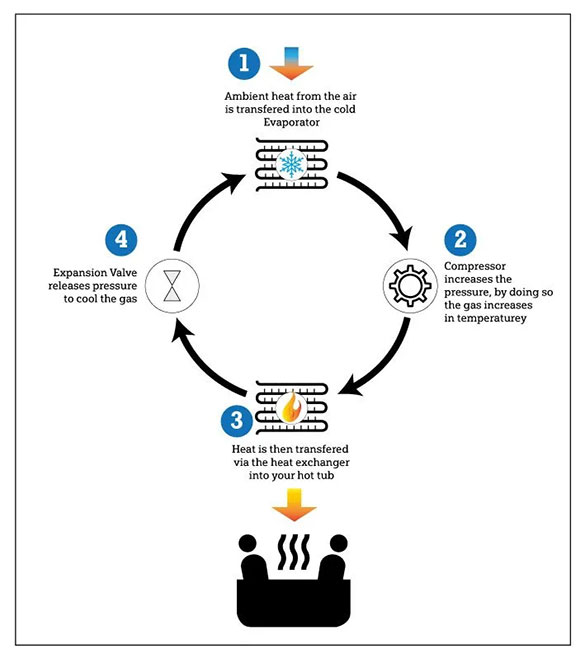
Heating Mode: In heating mode, a heat pump extracts heat from the outside air, ground, or water, and pumps it indoors.
Cooling Mode: In cooling mode, it reverses the operation, extracting heat from inside and expelling it outside, effectively cooling the interior.


Energy Efficiency:
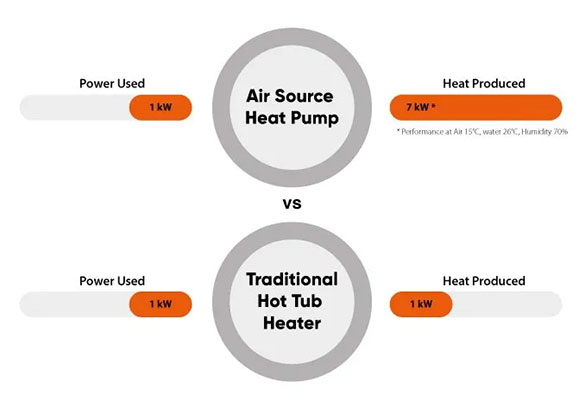
Heat pumps are up to 75% more energy-efficient than traditional electric or gas heaters.
They use electricity to move heat rather than generate it, which can result in significant cost savings over time.